Medici Family
The House of Medici was a powerful family from the Mugello region of Tuscany, who rose to prominence under Cosimo de' Medici. They were one of the wealthiest and most powerful families in Europe. In 1433, the Italian city-states were threatened by invasion from the Ottoman empire; in order to raise funds for troops, Cosimo closed his banks until a military force could be put togheder. This action saved the Italian states, and they came to rely on his economic wisdom.
Their Influence Lasted over 500 Years
The Medici family was a politically active and economically powerful Florentine banking family. The Medicis were one of the most important families of Italy during the Renaissance, and their influence extended across Europe. Political power and wealth allowed the Medicis to patronize numerous Italian artists and support other initiatives such as architecture and science that helped to shape the cultural landscape of Italy.
In general, the Medici liked to influence politics from behind the scene and used their wealth and connections to achieve their goals. In 1434 Cosimo the Elder was elected as one of the leaders of the Florentine Republic, and although he was only one of several men who ruled the city, he came to dominate it. His grandson Lorenzo de'Medici (1449-1492), known as Lorenzo Il Magnifico, became one of Italy's most famous patrons of arts.
They became “Godfathers of the Renaissance”
The Medici have had a significant impact on the history of art, and the most important legacy of their patronage is arguably Florence itself. They sponsored some of the greatest artists in Western civilization. In fact, a large number of the city's most notable works were made possible by their support.
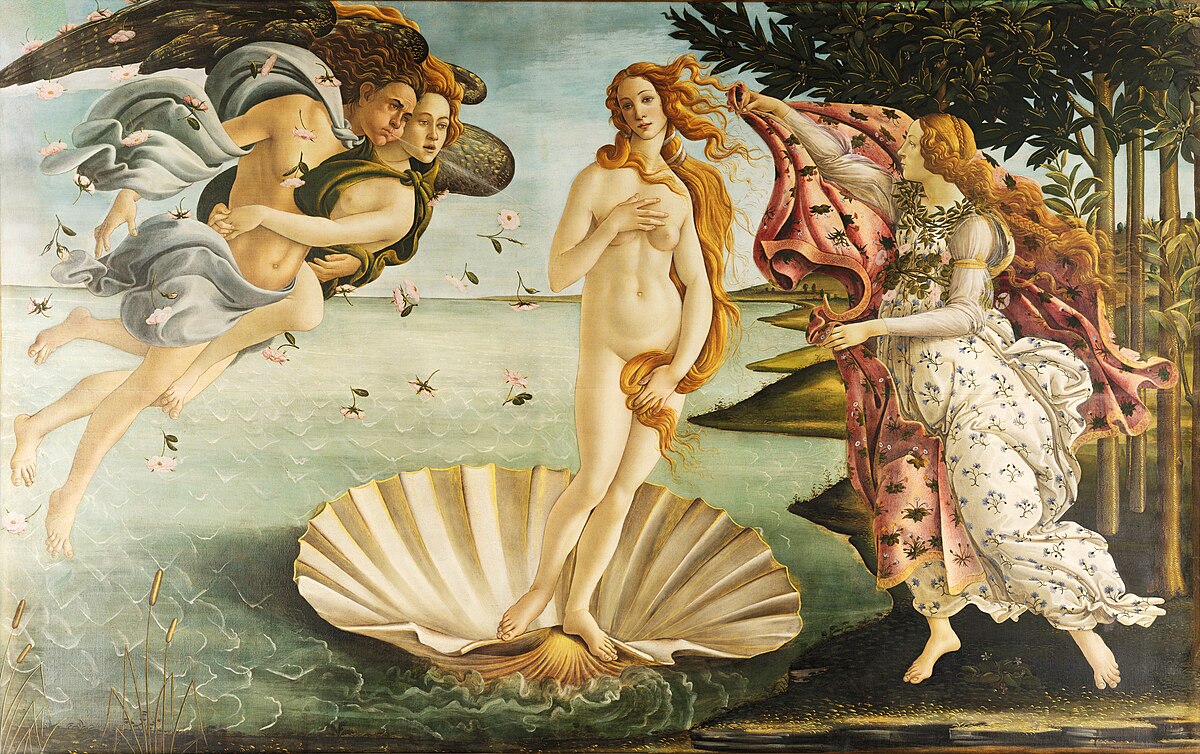
They helped to develop the Early and High Renaissance in Florence and Tuscany by sponsoring artists such as Botticelli, Michelangelo, Raphael, and da Vinci, who would become some of the most influential artists in all Europe.
Their influence was not limited to Italy and they had a great impact on art throughout Europe. Their influence was long lasting because they supported artists during their lives and often commissioned works to be completed after their deaths.
They Supported Science
The Medici family has a long and illustrious history. They were known for their influence on the art world, public works projects, and innovative new styles in architecture. But did you know that they also played a role in modern science?
Although none of the Medici themselves were scientists, the family is well-known to have been the patrons of the famous Galileo Galilei, who tutored multiple generations of Medici children and was an important figurehead for his patron's quest for power. Galileo's patronage was eventually abandoned by Ferdinando II, when the Inquisition accused Galileo of heresy. However, the Medici family did afford the scientist a safe haven for many years. Galileo named the four largest moons of Jupiter after four Medici children he tutored, although the names Galileo used are not the names currently used.
There were four popes who were related to the Medici.
Popes served as de facto political rulers of Rome, Florence, and large swaths of Italy known as the Papal States. The two closest related were Leo X and Clement VII.
The Church was not just one of the wealthiest institutions in the world, but also a major global diplomatic force. The papacy controlled vast tracts of land in Italy, France, Spain, and other countries. The pope was the arbiter of kings and queens and a key political power broker.
Social significance of fashion
Florence’s strong international trade links and ability to create innovative products, both reacting to and shaping consumer demand, meant that it became a major trading city in the 14th century. The Florentine wool and silk guilds were influential commodities, and the export of cloth was vital for the economy. Alongside banking, the wool and silk industries were key to Florence’s extraordinary wealth.